|
Work Title |
Goal/Application |
Method/Achievement |
Illustration |
|
Thermal Face Recognition |
- To develop a reliable thermal face recognition system for national security applications;
- Typical Applications: Prevention against terrorism at airports and borders,
especially at nighttime;
- Authentification to access a federal building or a computer-controlled device or facility.
|
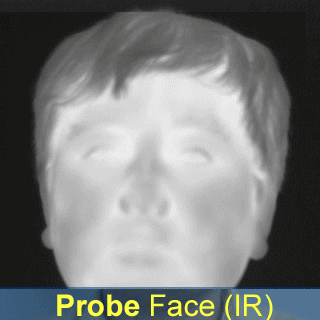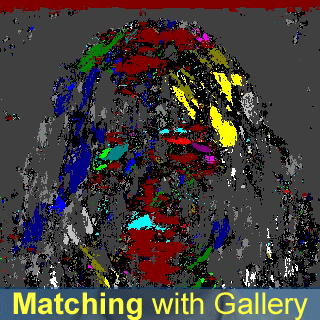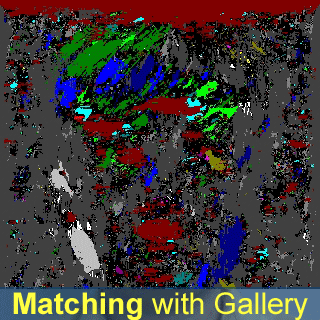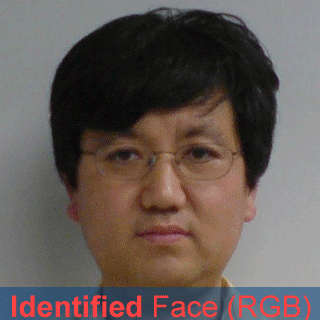
- A new orientation-based face recognition method is proposed, which utilizes Gabor wavelet transform and Hamming distance for identification;
- The identification rate of the proposed method (called "Face Pattern Byte") achieves 97.92% with
one modality image, and 100% with the score fusion of two modality images.
|
 |
|
Night Vision Colorization |
- To enhance computer vision and human vision by multispectral image fusion and night vision colorization;
- Applications: Performance improvement of night-time operation, surveillance and navigation, target recognition,
and situational awareness;
- Enhancement of national security.
|
- The image fusion is based on the advanced DWT transform, and further
optimized with regard to an IQ metric via an iterative DWT procedure;
- The colorization is accomplished by mapping the color statistics of each segment
in the multispectral (i.e., night vision) imagery to that of the auto-selected daylight
picture;
- A channel-based color fusion method is proposed for real time applications;
- A quantative metric is proposed to measure and compare the image quality of
colorized images.
|
 |
|
Breast Cancer Detection |
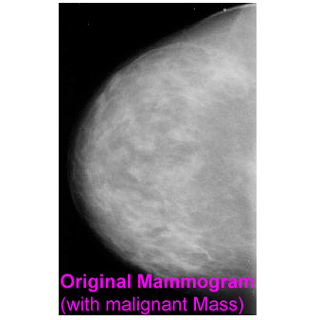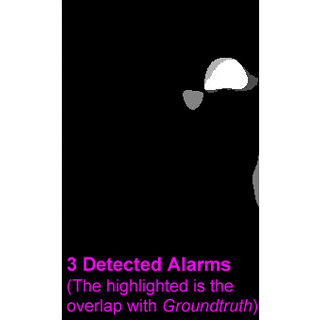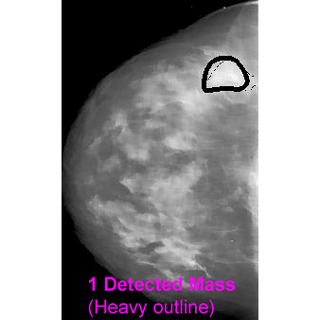
- To detect breast cancers using digitized mammograms at their early stages;
- The lifetime risk of developing breast cancer among American women is 13.4% (one in seven), exceeded only by lung cancer;
- With digital mammograms computer-aided detection (CAD) is very useful to radiologists (as "a second pair of eyes").
|
- A new breast cancer detection algorithm utilizing Gabor features is proposed,
which involves in preprocessing, segmentation (generating alarm segments), and
classification (reducing false alarms);
- The proposed algorithm achieved TP (true positive rate) = 90% at FPI (false
positives per image) = 1.21 in mass detection; and TP = 93% at FPI = 1.19 in
calcification detection.
|
 |
Bioinspired Color Enhancement
|
- To simulate the contrast enhancement of center/surround networks and opponent analysis on the human retina;
- The human retina ahs two center/surround layers, bipolar/horizontal and
ganglion/amacrine; and four color opponents, red (R), green (G), blue (B), and
yellow (Y);
- The bio-inspired model is a powerful tool for image analysis and pattern recognition.
|
- In our proposed enhancement model, the surrounding information is obtained using weighted average of neighborhood; excited or inhibited can be implemented with pixel intensity increase or decrease according to a linear or nonlinear response; and center/surround excitations are decided by comparing their intensities.
- A difference of Gaussian (DOG) model is used to simulate the ganglion differential response.
- The image quality of enhanced results is overall satisfied.
|
 |
|
Glaucoma Detection |
- To detect glaucoma in its earliest stages by applying shape-based analysis
techniques of retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness to GDx-VCC (variable
corneal and lens compensator) polarimetry data.
|
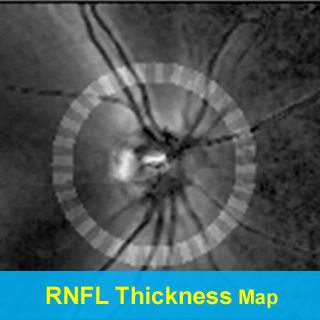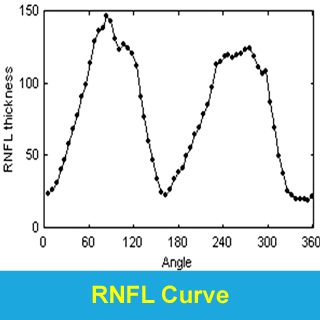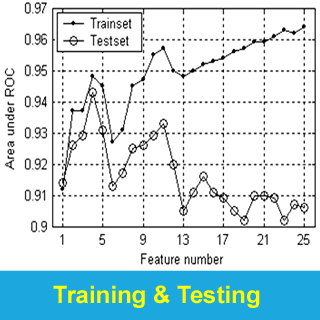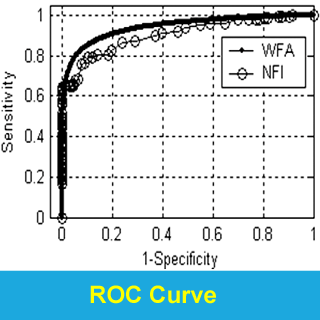
- Wavelet-based (wavelet-Fourier analysis
[WFA]), Fourier-based (fast Fourier analysis [FFA]),
as well as the standard metric nerve fiber indicator
(NFI), and all were compared as a function of disease stage;
- Classification performance of WFA (ROC = 0.978; recently proposed method)
was significantly better than FFA (ROC = 0.938) and NFI
(ROC = 0.900).
|
 |


